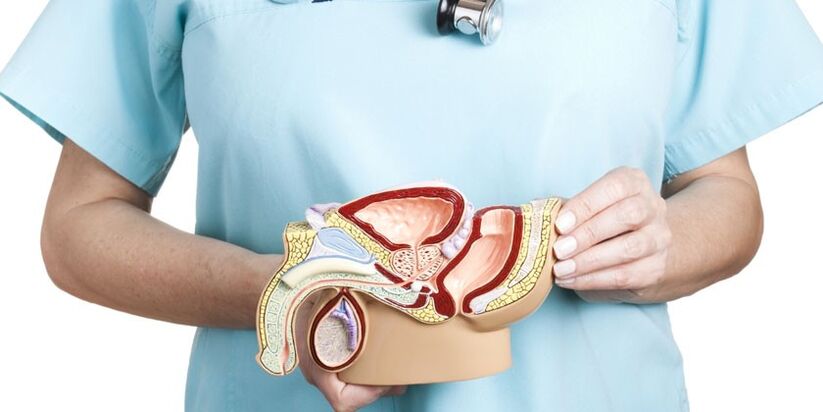
According to statistics, more than 75% of men over the age of 40-45 suffer from prostate diseases. Strong circulation of lymph and blood in the vessels of the small pelvis often leads to swelling of the organ and congestion. In addition, the prostate is well innervated, so the symptoms of the disease in men include severe pain.
What is the prostate
The prostate or prostate gland is the male reproductive organ, part of the reproductive system. Located in the small pelvis below the bladder, it partially covers the urethra and ejaculatory ducts. The prostate consists of two lobes and an isthmus connecting them. In addition, the upper, lower, front and rear parts are distinguished in the organ. The shape of the prostate resembles a chestnut, is elastic and consists of glandular and muscle cells. The prostate performs three main functions:
- Engine. The muscle cells of the prostate form a sphincter muscle in the urethra that holds the urine.
- Office. The gland produces a special secret that gives sperm mobility and liquefies the sperm.
- Barrier. Prevents the spread of infections from the urethra.
prostate disease in men
Pathologies are usually associated with damage to the organ by pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms, congestion or neoplasms (both malignant and benign). >Diseases of the prostate include:
- inflammation (prostatitis);
- benign hyperplasia of the gland (adenoma);
- malignant neoplasm (cancer);
- cystic neoplasms;
- prostate abscess.
Many factors that create a favorable environment and conditions for the penetration and reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms (fungi, viruses, bacteria) can provoke the beginning of the development of pathologies and signs of inflammation of the prostate in men. In addition, they can cause the development of benign or malignant tumors. Unfavorable factors are:
- malnutrition;
- hypovitaminosis;
- STDs;
- hypothermia of the body;
- hypodynamia;
- long-term antibiotic treatment;
- congestion in the pelvis;
- Bad habits;
- endocrine pathologies;
- pathology of the reproductive system;
- oncological diseases in history;
- persistent fatigue.
Symptoms of prostate disease in men
Signs of prostate dysfunction depend on the cause of the disease, its localization and the nature of the pathological processes. As a rule, the patient complains of weakness, reduced performance, general fatigue and irritability. In addition, symptoms of prostatitis and prostate adenoma in men, stones or abscesses can manifest themselves as follows:
- violation of urination;
- erectile dysfunction;
- Infertility;
- pain, burning in the urethra;
- temperature rise;
- Chills;
- painful intercourse;
- lack of ejaculation;
- pain in the perineum with sudden movements;
- offensive discharge from the urethra.
prostatitis
The inflammatory lesion of the prostate, prostatitis, is one of the most common diseases of the male genital area. The main cause of the pathology is considered a violation of blood circulation in the pelvis, which leads to a sharp increase in the proportions of the organ and its edema. The symptoms of prostate inflammation depend on the type of disease. There are several types of pathologies:
- acute inflammation. Caused by pathogenic microbes (e. g. E. coli or enterobacteria). Acute prostatitis is manifested by severe pain and pain in the urethra, impaired urination: urine is excreted with difficulty, sometimes drop by drop. Some patients report an increase in temperature.
- Chronic bacterial inflammation. It is usually caused by sexual infections (chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, etc. ). Symptoms of chronic inflammation of the prostate can be mild or absent. Among the characteristic signs, sexual dysfunction (erectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation), painful urination (mainly nocturnal) and discharge of mucus from the urethra are noted.
- Chronic non-bacterial inflammation. The disease develops as a result of inflammatory processes in other organs (pyelonephritis, cystitis), blood stagnation, heart failure, hypothermia. Such prostatitis often has one symptom - difficulty urinating. Often the result of the pathology is a violation of the kidneys, discomfort in the lower back.
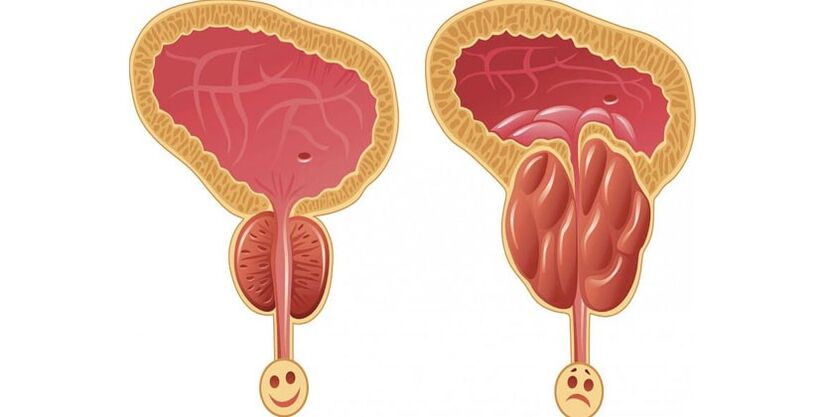
BPH
A disease of the prostate characterized by benign tissue growth and the formation of nodules that gradually compress the urethra and vas deferens, the bladder. Hyperplasia can lead to a violation of the concentration of hormones in the blood. The signs of prostate adenoma in men vary depending on the stage of the disease:
- compensated. As a rule, men at this stage do not notice any specific symptoms. Sometimes there is an increased urge to urinate at night.
- undercompensated. The main symptoms are a feeling of heaviness in the bladder, its incomplete emptying. Liquid when urinating is difficult to pass, patients complain of difficult ejaculation.
- decompensated. It is characterized by a significant decrease in the volume of the muscles of the bladder and their tone. In addition, the adenoma develops chronic fatigue, pain, and spasms when attempting to urinate. Without treatment, tumor growth, pain intensity increases significantly, defecation can be disrupted by compression of the rectum.
Prostate adenoma is considered a precancerous condition. Therefore, when this tissue growth is detected, a biopsy is required to detect atypical cells and ultrasound (ultrasound) to study the structure of the organ in detail. Hyperplasia of the gland, as a rule, progresses slowly, which allows timely diagnosis and treatment.
cyst
Under the influence of inflammatory processes of the gland, a pathological cavity with fluid or a prostate cyst develops, in which the excretory ducts of the organ are squeezed and the outflow of secretions is disturbed. Pathology can be provoked by constant stress, nerve strain, chronic diseases and tumors of neighboring organs, sclerosis of the prostate tissue. Signs of cyst formation are:
- burning in the urethra;
- enlargement of the gland in size;
- decreased libido;
- increase in body temperature;
- feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder;
- reproductive dysfunction.
stones
The formation of stones in the prostate occurs due to a sedentary lifestyle, injuries in the groin, inflammatory diseases of the organ. With increasing size, the stones violate the integrity of the gland ducts, urine begins to penetrate the prostate tissue. Stones usually consist of phosphates, salts of uric and oxalic acids, protein and epithelium of the ducts. The main signs of pathology are:
- weak erection;
- pain when urinating;
- frequent exacerbations of inflammation;
- pain during ejaculation;
- Seals in gland and pain when probed.
Cancer
A malignant growth that develops from the secretory epithelium of the prostate is called a cancer or carcinoma. Prolonged inflammatory processes precede the development of the tumor. The risk group includes men over 40 who abuse alcohol and smoke. Symptoms of oncological damage to the prostate are nonspecific and are expressed in a violation of the functioning of the organ. In the early stages, the disease usually does not manifest itself. With the development of the tumor, the following symptoms develop:
- hematuria;
- painful urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- swelling of the legs;
- violation of the stool;
- Impotence.
abscess
An infectious-inflammatory pathology accompanied by purulent fusion of tissues is called an abscess. Such a process develops due to the transmission of pathogenic bacteria from the primary focus of infection to the prostate through the bloodstream. An abscess can be asymptomatic for a long time. The main signs of the presence of a purulent focus in the tissues of the prostate are: >
- fever and fever;
- painful intercourse, urination;
- Passing of foul-smelling pus in the urine (when an abscess ruptures).
Purulent formation in the prostate is diagnosed with the help of instrumental and laboratory studies. During blood tests, an increase in the number of leukocytes and an increase in the value of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate are detected. When examining urine, leukocyturia and pathogenic microflora are detected. Palpation examination through the rectum shows the presence of a rounded formation.
The main methods of treating the prostate
Methods of treating pathologies depend on the specific disease, the stage of its course and severity. Therapy for prostate diseases is selected individually, depending on the patient's age, the results of laboratory tests, instrumental studies and the presence of concomitant diseases. Familiarize yourself with the basic principles of treating prostate diseases:
illness |
treatment methods |
|---|---|
prostatitis |
|
adenoma |
|
cyst |
|
stones |
|
Cancer |
|
abscess |
|
prevention
To prevent the development of prostate diseases, you should follow the principles of a healthy lifestyle. Reduces the risk of prostate pathologies by following the recommendations:
- Stick to a balanced diet.
- Move regularly.
- Take multivitamin complexes, immunomodulatory drugs.
- Avoid alcohol, tobacco, drugs.
- Avoid hypothermia.
- See your doctor as soon as symptoms appear.